The Future of Food: Vertical Farming and Cultured Meat
In the shadows of a looming global food crisis, two groundbreaking innovations are emerging as beacons of hope: lab-grown meat and vertical farming. These technologies promise to drastically reduce the environmental footprint of food production and reshape our understanding of sustainable agriculture.
Cultured Meat: A Meaty Revolution Without the Environmental Cost
Cultured or lab-grown meat is produced by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment. This technology can seriously reduce greenhouse gas discharge, land requirements, and water squandering associated with traditional livestock farming. A study by the University of Oxford and the Amsterdam University of Applied Sciences highlights that lab-grown meat could reduce energy use by up to 45%, greenhouse gas discharge by 96%, and land use by 99% compared to conventional meat production.
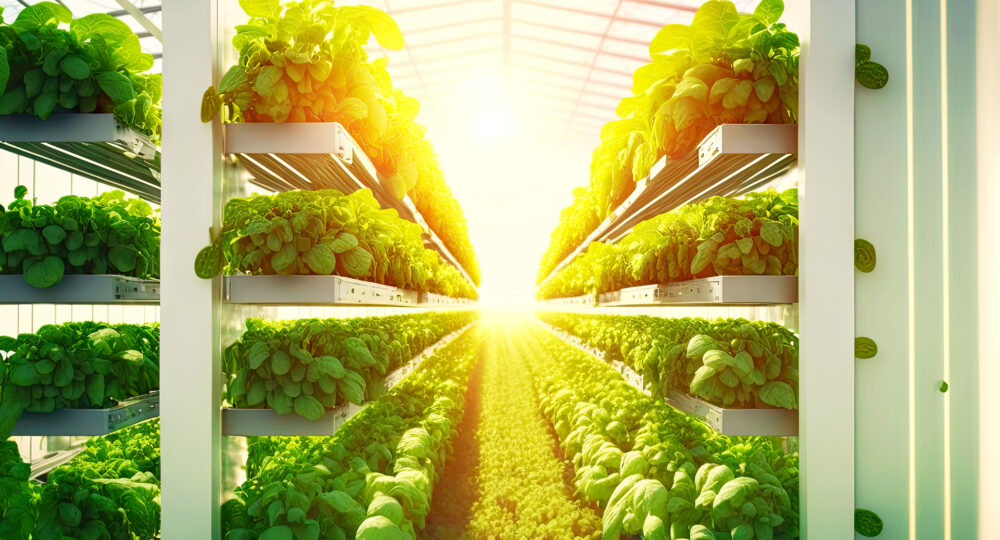
The Rise of Vertical Farming: Agriculture Reaches New Heights
Vertical farming takes the concept of agriculture to new heights, quite literally. By stacking crops in vertically aligned layers and using controlled environments, these farms can produce crops year-round, irrespective of weather conditions. This method optimizes space, minimizes water usage, and eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides. According to the American Society for Horticultural Science, vertical farming can yield up to 10 times more per unit area than traditional farming.
The Synergy of Technology and Nature
Both lab-grown meat and vertical farming rely heavily on technological advancements. Lab-grown meat utilizes bioreactors and tissue engineering techniques, while vertical farming incorporates hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics coupled with LED lighting and climate control systems. This synergy of technology and nature is not just about producing food; it’s about redefining the efficiency and sustainability of food production.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite their potential, both technologies face their own set of challenges. Lab-grown meat must grapple with high production costs and consumer acceptance issues. Similarly, vertical farming requires significant initial investment and energy consumption, raising questions about its sustainability.
The Road Ahead
As we move forward, it’s clear that lab-grown meat and vertical farming will play critical roles in shaping the future of food. They offer solutions to some of the most crucial issues of our time, including food safety policy, environmental dissipation, and the ethical treatment of animals. With continued research and development, these innovations could be at the forefront of a food revolution.
The future of food is unfolding before our eyes, marked by lab-grown meat and vertical farming. These technologies offer a glimpse into a world where food production is sustainable, efficient, and in harmony with the planet. As we embrace these innovations, we step closer to a future where the global food crisis is a thing of the past.
References:
- Environmental impacts of cultured meat production by Hanna L. Tuomisto and M. Joost Teixeira de Mattos, University of Oxford.
- Resource use efficiency and environmental performance of nine major biofuel crops, processed by first-generation conversion techniques by the American Society for Horticultural Science.
- Cultured meat from stem cells: Challenges and prospects by Mark J. Post, Maastricht University.